Safety Element
Overview
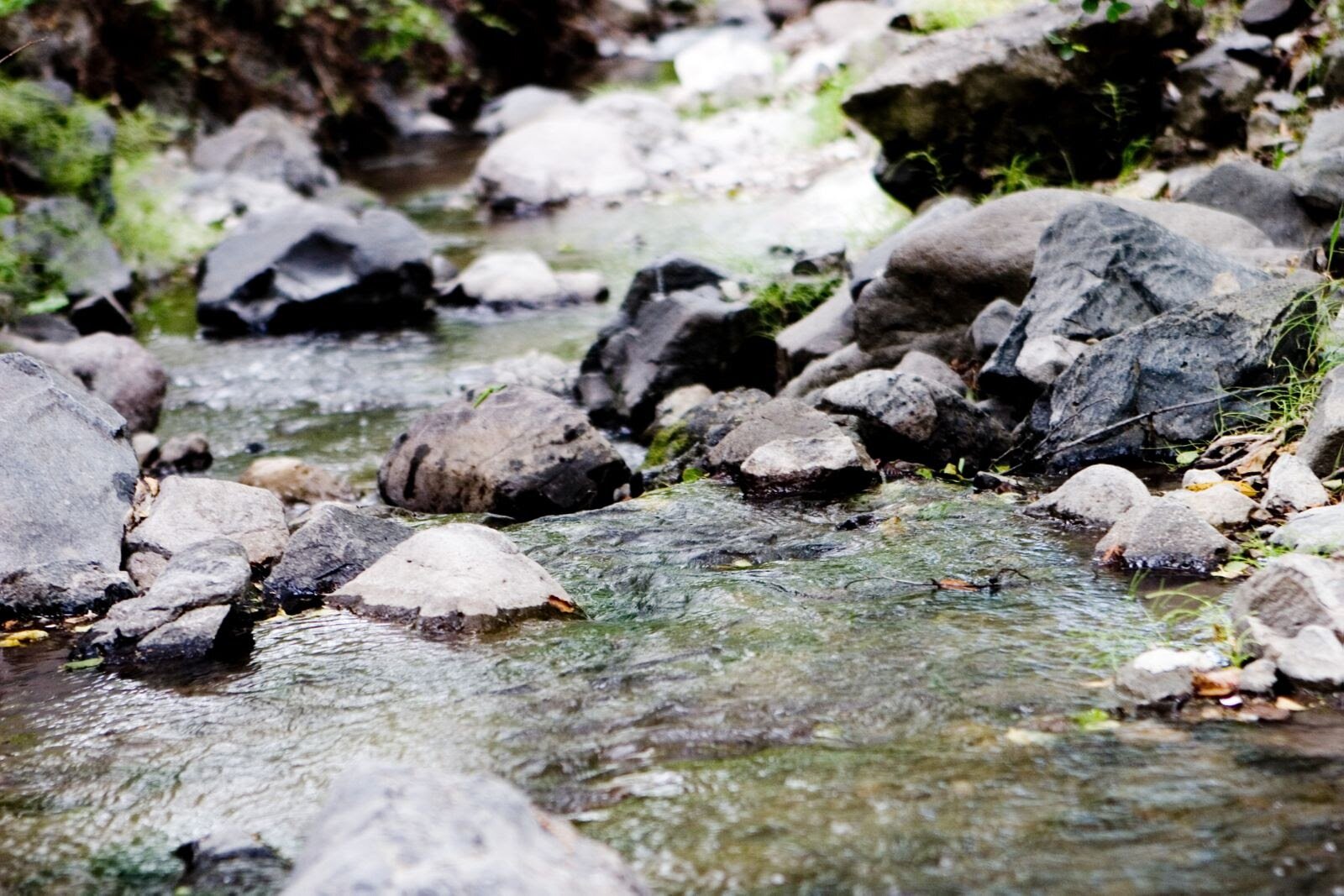
The purpose of a Safety Element is to include safety considerations in the planning and decision-making process by establishing policies related to future development. The Safety Element, a requirement element of the City’s General Plan, identifies natural and man-made hazards that may result in personal injury, loss of life, property damage, or environmental damage. Since 2012, there have been several updates to Safety Element requirements to include climate change vulnerability and adaptation and greater attention to wildlife and evacuation routes. Pursuant to Senate Bill (SB) 1035, all local jurisdictions in California must update their Safety Element upon each revision of the Housing Element or Local Hazard Mitigation Plan, but not less than once every 8 years. Orinda’s Safety Element update is occurring concurrently with the Housing Element update.
Prior Safety Element
Orinda’s prior Safety Element provides a brief discussion of risks (including seismic activity, landslides, flood hazard, fire protection, hazardous materials and evacuation routes) and identifies guiding and implementing policies. The Safety Element had not had a comprehensive update since the City’s general plan was adopted in 1987. It was last amended in 2011 to incorporate policies related to the Local Hazard Mitigation Plan.
Local Hazard Mitigation Plan
Pursuant to the Disaster Mitigation Act of 2000, local jurisdictions are required to prepare a Local Hazard Mitigation Plan (LHMP) in order to qualify for federal funding for disaster mitigation activities. LHMPs look at hazards that affect local jurisdictions and suggests mitigation actions to reduce losses from those hazards. Orinda’s LHMP was last updated and adopted by the City Council in 2018. The 2018 LHMP was prepared as part of a multi-jurisdictional planning document with a coalition of 35 Contra Costa County cities and special districts. LHMP’s must be updated every five years.
Evacuation Analysis
On March 15, 2022, the City Council authorized the preparation of an Evacuation Route Analysis as part of the Safety Element. While the Safety Element is required to include a general discussion of emergency evacuation, the Evacuation Analysis provides a deeper analysis of emergency scenarios and evacuation roadways. The evacuation analysis is conducted in compliance with AB 747 which requires jurisdictions to identify and evaluate the capacity, safety, and viability of evacuation routes under potential emergency scenarios. While AB 747 requires evacuation analyses to be completed as part as an LHMP update, the expanded evacuation analysis was added to the Safety Element based on community interest in emergency preparedness and evacuation. The evacuation analysis evaluates three wildfire scenarios as well as potential landslide risk along possible evacuation routes.
Safety Element Components
Wildland and Urban Fires
Analyze fire hazard severity zone maps, historic data on wildfires, evacuation routes and the general location of existing and planned uses in very high fire hazard severity zones. Establish a set of goals, policies and objectives for the protection from the unreasonable risk of wildfires.
Climate Change Adaptation & Resilience
Perform a vulnerability assessment that identifies the risks climate change poses and the geographic areas at risk from climate change impacts. Create a set of adaptation and resilience goals, policies and objectives based on the vulnerability assessment.
Flooding
Identify flood hazard zones, areas subject to inundation, and historic flood information. Create goals, policies and objectives that avoid and minimum flood risks for new development, maintain the integrity of essential public facilities and establish working relationships with public agencies responsible for flood protection.
Other Considerations
Address interrelated considerations in the context of fire and geological hazards. This includes military installations, peakload water supply requirements, and minimum road widths and clearances around structures.
Seismic Risks
Understand historical data on landslides and mudslides. Determine and evaluate the location of active fault zones and potential for displacement along active and potentially active faults. Establish goals, policies and objectives to minimize the loss of property and life as a result of earthquakes.
Implementation Measures
Identify feasible implementation measures to carry out the goals, policies and objectives of each component of the safety element.
Adopted Vulnerability Assessment
The Vulnerability Assessment is a required component of the Safety Element Update. The Vulnerability Assessment as part of the Safety Element Update was adopted by the City Council on January 31, 2023.
Evacuation Analysis
The Evacuation Analysis analyzes roadways along evacuation routes that are likely to be most congested during an evacuation event, as well as residential areas that are most vulnerable to traffic congestion along the identified evacuation routes. The Evacuation Analysis is referenced in the Safety Element and specific goals and policies have been developed based on the analysis, but the final Evacuation Analysis document is a standalone document.